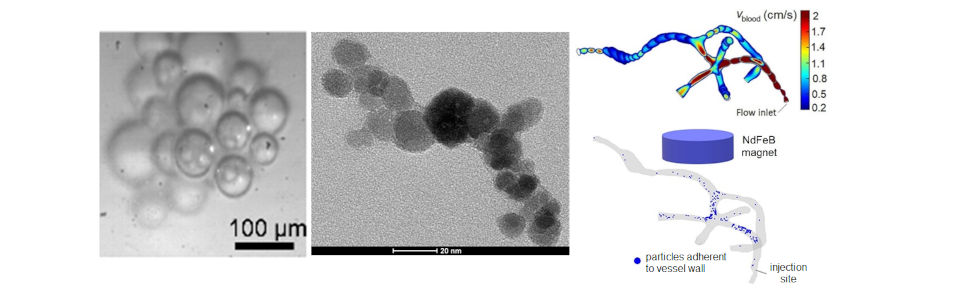
This sector studies nanomaterials for applications in magnetic hyperthermia, controlled drug delivery and diagnostic imaging.
In hyperthermia, magnetic nanoparticles are synthesised using in-solution techniques based on co-precipitation or thermal decomposition reactions, guaranteeing the process's scalability and reproducibility. Through micromagnetic numerical models, nanomaterials are designed with optimal properties for magnetic hyperthermia, focusing on the influence of shape, size and composition.
In silico models are also realised, which simulate the transport of magnetic nanoparticles in blood vessels, their release into tissues and their thermal effects, resulting from the application of alternating magnetic fields.
In drug delivery, perfluorocarbon (PFC)-based nanodroplets are prepared for the controlled release of oxygen through activation by ultrasound. Finally, multifunctional and multi-responsive nanomaterials are developed by functionalising nanodrops with magnetic nanoparticles.