The second, symbol s, is the SI unit of time. It is defined by taking the fixed numerical value of the caesium frequency ΔνCs, the unperturbed ground-state hyperfine transition frequency of the caesium-133 atom, to be 9 192 631 770 when expressed in the unit Hz, which is equal to s–1.
Definition from the new SI.
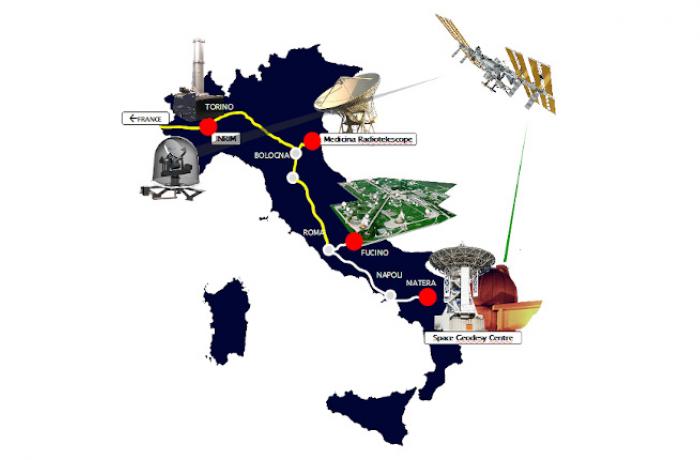
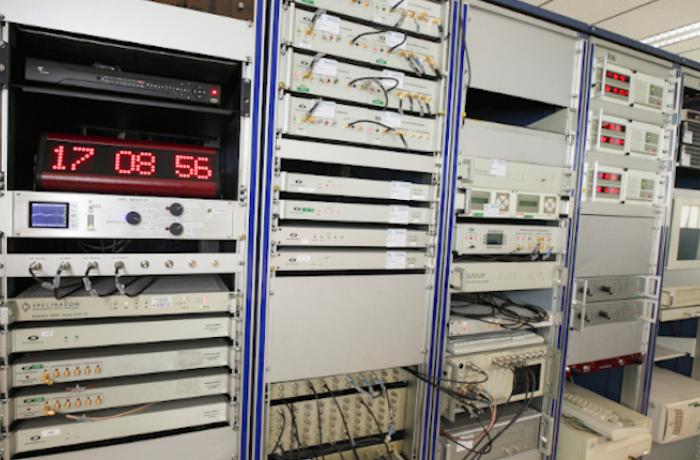
INRIM realizes the Italian primary frequency standard, based on a cesium fountain clock, nitrogen-cooled at 89 K. It has an accuracy of 2 10-16, among the highest ever achieved.
This clock is used for the generation of the Italian timescale and its data are periodically sent to the Bureau International des Poids et Mesures for the computation of the International Atomic Timescale.
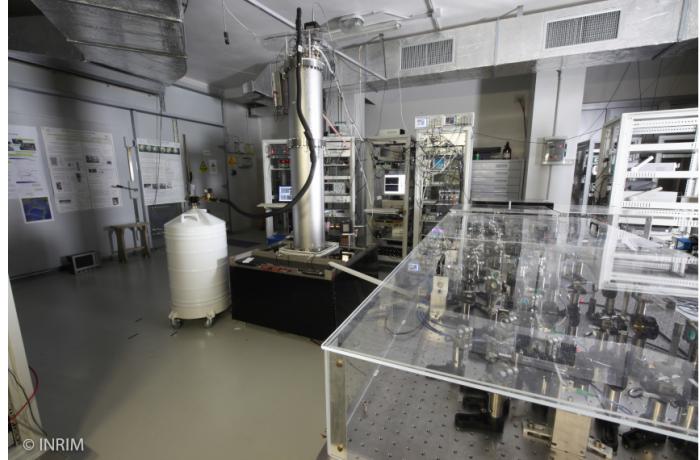


Optical frequency standards are the most promising candidates for the redefinition of the Second in the International System of Units, as they enable to achieve lower uncertainties than primary microwave clocks (cesium fountains).
We realized an Ytterbium optical lattice clock and we are developing a cavity-enhanced Strontium optical lattice clock.
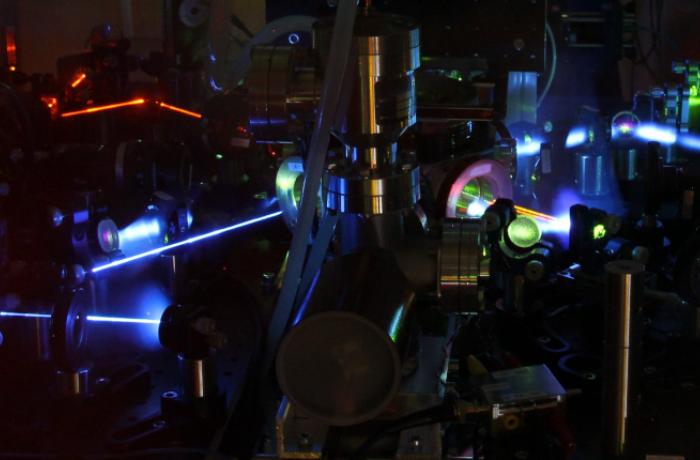
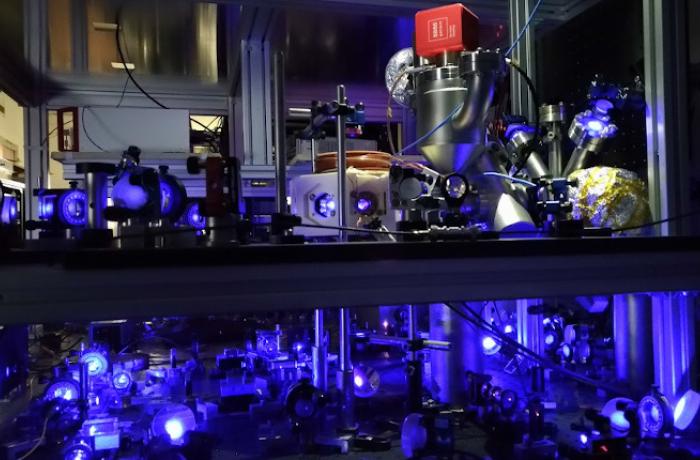
Time and frequency standards are disseminated via optical fiber to several research institutes of the country, to allow precise measurements in atomic and molecular physics at unprecedented resolution, and to commercial and industrial stakeholders.
INRIM also participates in the European satellite navigation system Galileo.